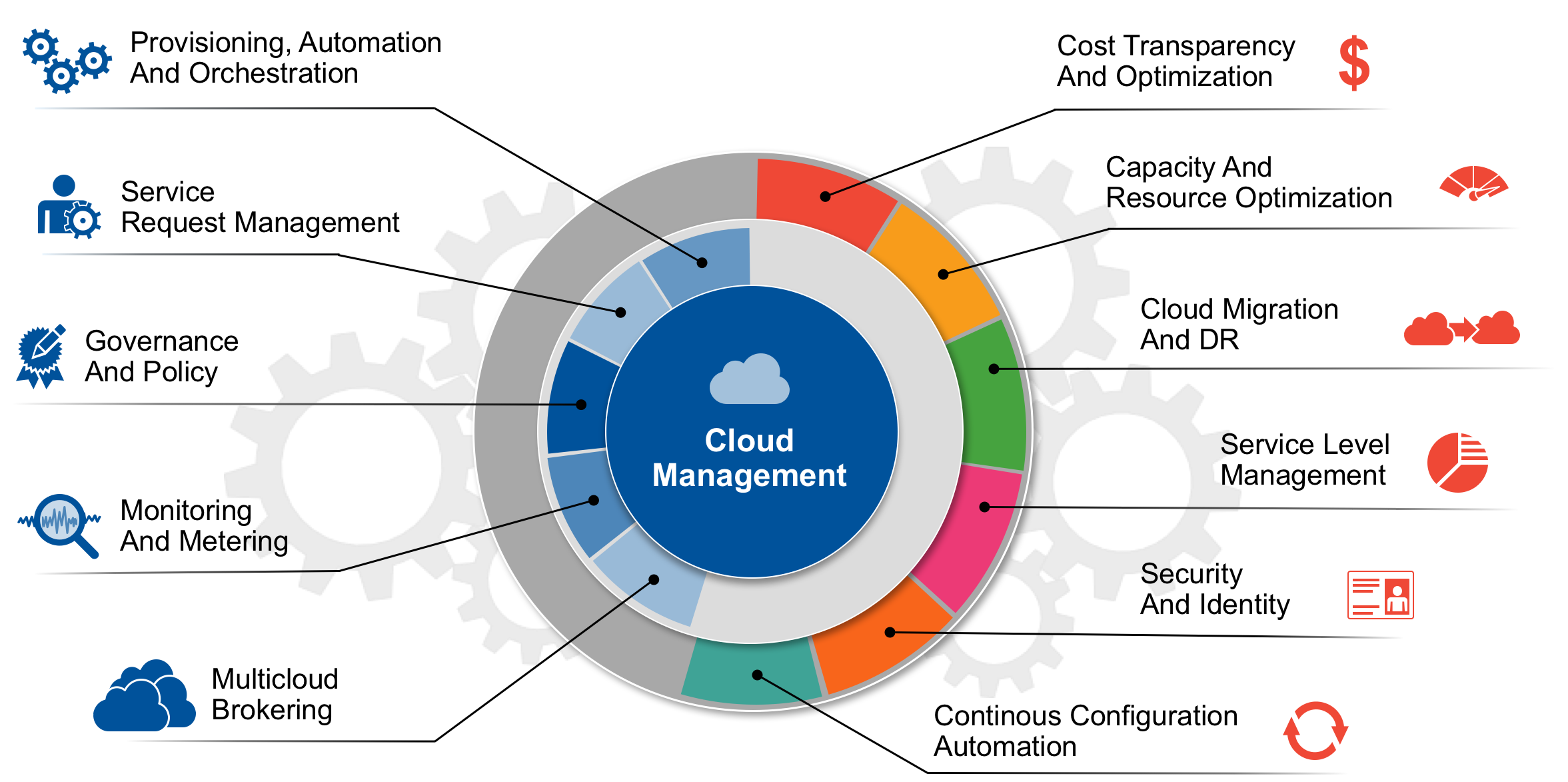
Cloud management refers to the process of overseeing and controlling the resources, services, and applications that are deployed on cloud computing infrastructure. It involves the management of various aspects of cloud computing, including cloud resources, virtual machines, storage, networking, and security.
Cloud management encompasses a range of activities and tasks, such as:
- Provisioning and deployment: This involves creating and configuring virtual machines, storage resources, and networking components in the cloud environment.
- Resource allocation and optimization: Cloud management involves monitoring resource utilization, optimizing resource allocation to ensure efficient usage, and scaling resources up or down based on demand.
- Monitoring and performance management: It includes monitoring the performance and availability of cloud resources and applications, identifying bottlenecks or issues, and taking proactive measures to maintain optimal performance.
- Security and compliance: Cloud management involves implementing security measures to protect cloud resources and data from unauthorized access, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards, and managing user access and permissions.
- Cost management: It includes tracking and managing cloud costs, optimizing resource usage to minimize expenses, and implementing cost allocation and budgeting mechanisms.
- Backup and disaster recovery: Cloud management involves setting up and managing backup and disaster recovery mechanisms to ensure data protection and business continuity in case of failures or disruptions.
- Automation and orchestration: Cloud management often involves automating routine tasks and workflows, using scripting or orchestration tools to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
Cloud management can be performed using various tools and platforms, including cloud management platforms (CMPs), cloud service provider-specific management consoles, and third-party management tools. These tools provide centralized control and visibility over cloud resources, enabling organizations to effectively manage their cloud infrastructure and applications.
How does cloud management work?
Cloud management works by providing a centralized platform or set of tools that allow organizations to manage and control their cloud resources, services, and applications. Here’s a general overview of how cloud management works:
- Provisioning and Deployment: Cloud management tools enable users to provision and deploy cloud resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking components, through an intuitive interface or programmatically via APIs. These tools handle the underlying infrastructure provisioning, ensuring that the necessary resources are allocated and configured according to the user’s requirements.
- Resource Monitoring and Optimization: Cloud management platforms continuously monitor the utilization and performance of cloud resources and applications. They collect data on resource usage, network traffic, application performance metrics, and other relevant information. This data is analyzed to identify any bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or potential issues. Based on these insights, administrators can optimize resource allocation, scale resources up or down, and make informed decisions to improve overall performance and efficiency.
- Security and Compliance: Cloud management tools provide features and functionalities to ensure the security and compliance of cloud environments. They offer mechanisms for managing user access and permissions, implementing security policies, and monitoring for security threats or vulnerabilities. Compliance frameworks and standards can be enforced through the management tools, allowing organizations to meet regulatory requirements.
- Cost Management: Cloud management platforms help organizations manage their cloud costs effectively. They provide visibility into resource usage and associated costs, allowing administrators to track expenses, identify cost-saving opportunities, and optimize resource allocation to minimize expenses. Budgeting and cost allocation mechanisms can also be implemented to allocate costs to specific departments or projects.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Cloud management platforms often include features for backup and disaster recovery. They enable users to set up automated backup schedules, define retention policies, and facilitate the restoration of data in case of data loss or system failures. Disaster recovery mechanisms can be configured to ensure business continuity by replicating data and applications across multiple cloud regions or availability zones.
- Automation and Orchestration: Cloud management tools support automation and orchestration of tasks and workflows. They provide scripting capabilities, APIs, or integration with other tools to automate routine tasks, such as resource provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment. Orchestration allows administrators to define and manage complex workflows across multiple cloud resources or services, ensuring efficient and consistent operations.
Cloud management can be performed using a combination of in-house tools, cloud service provider-specific management consoles, or third-party cloud management platforms. The choice of tools depends on the specific requirements of the organization and the cloud infrastructure they use.
What are the benefits of cloud management?
Cloud management offers several benefits for organizations that leverage cloud computing. Some of the key benefits include:
- Centralized Control and Visibility: Cloud management provides a centralized platform or set of tools that offer administrators and IT teams a unified view and control over their cloud resources. This centralized control and visibility simplify the management of complex cloud environments, allowing for efficient resource allocation, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud management enables organizations to scale their cloud resources up or down based on demand. It provides the ability to provision additional resources quickly and easily, allowing for agility and flexibility in adapting to changing business requirements. This scalability helps organizations avoid overprovisioning or underutilization of resources, optimizing costs and performance.
- Cost Optimization: Cloud management tools and platforms offer features to monitor and optimize cloud costs. Administrators can track resource usage, identify cost-saving opportunities, and implement strategies to optimize resource allocation and utilization. This helps organizations maximize their return on investment in cloud infrastructure and services.
- Improved Performance and Availability: Cloud management facilitates performance monitoring and optimization, ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently and applications perform optimally. It enables proactive monitoring and alerting to detect and resolve performance issues promptly. Additionally, cloud management tools often include built-in high availability and disaster recovery mechanisms to enhance the availability and resilience of applications and data.
- Enhanced Security and Compliance: Cloud management platforms provide features to enforce security measures, manage user access and permissions, and monitor for security threats. They help organizations maintain the security of their cloud environments and meet regulatory compliance requirements. Cloud management tools often offer integration with security tools and services to strengthen overall security posture.
- Automation and Streamlined Operations: Cloud management enables automation and orchestration of routine tasks and workflows, reducing manual efforts and human errors. Administrators can automate resource provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment, among other tasks. This automation streamlines operations, increases efficiency, and frees up resources for more strategic initiatives.
- Collaboration and DevOps Enablement: Cloud management platforms often support collaboration among teams and facilitate DevOps practices. They provide features for version control, code deployment, and integration with continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. This enables cross-functional teams to collaborate seamlessly and deliver applications faster and more efficiently.
Cloud management empowers organizations to leverage the full potential of cloud computing while ensuring efficient resource utilization, cost optimization, security, and scalability. It simplifies the management of complex cloud environments, enabling organizations to focus on their core business goals and innovation
What should a cloud management platform do?
A cloud management platform (CMP) should provide a comprehensive set of features and capabilities to effectively manage and control cloud resources, services, and applications. Here are some key functionalities that a cloud management platform should ideally offer:
- Resource Provisioning and Deployment: The CMP should enable users to provision and deploy cloud resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking components, in a self-service manner. It should offer an intuitive interface or APIs for resource provisioning, allowing users to easily configure and launch cloud instances based on their requirements.
- Resource Monitoring and Optimization: The CMP should provide monitoring capabilities to track the performance, utilization, and health of cloud resources. It should collect data on resource usage, network traffic, and application performance metrics, and offer real-time visibility into the state of the cloud infrastructure. The platform should also provide optimization features to identify inefficiencies, recommend resource allocation adjustments, and facilitate scaling of resources based on demand.
- Cost Management and Optimization: The CMP should include features to monitor and manage cloud costs. It should provide insights into resource usage and associated costs, allowing administrators to track and optimize expenses. The platform should support budgeting, cost allocation, and showback/chargeback mechanisms to allocate costs to specific projects or departments. It should also offer tools to identify cost-saving opportunities, such as resource rightsizing and utilization optimization.
- Security and Compliance: The CMP should support security measures to protect cloud resources and data. It should provide features for managing user access and permissions, enforcing security policies, and monitoring for security threats. The platform should also help organizations achieve compliance with industry regulations and standards, offering built-in or integratable controls for data privacy, encryption, identity and access management, and audit trails.
- Automation and Orchestration: The CMP should enable automation and orchestration of cloud operations and workflows. It should support scripting, APIs, and integration with other tools, allowing users to automate routine tasks, configuration management, and deployment processes. The platform should facilitate the creation of workflows and automation scripts to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce manual efforts.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: The CMP should include features for backup and disaster recovery to ensure data protection and business continuity. It should offer mechanisms for automated backup, restore, and recovery of cloud resources, allowing organizations to easily recover from data loss or system failures. The platform should support replication, snapshotting, and backup scheduling for different types of cloud resources.
- Governance and Policy Management: The CMP should provide capabilities for governance and policy enforcement. It should allow administrators to define and enforce policies related to resource provisioning, security, compliance, and cost management. The platform should enable organizations to set up approval workflows, policy-based resource restrictions, and governance controls to ensure adherence to internal policies and best practices.
- Integration and Ecosystem Support: The CMP should offer integration capabilities with various cloud service providers and technologies. It should support multiple cloud platforms, allowing organizations to manage hybrid and multi-cloud environments from a single interface. The platform should also provide integration with external tools and services, such as configuration management systems, monitoring solutions, and CI/CD pipelines, to enable seamless workflows and collaboration.
Overall, a cloud management platform should provide a unified and user-friendly interface to manage, monitor, optimize, secure, and automate cloud resources and services. It should empower organizations to efficiently leverage cloud computing while ensuring governance, cost control, and compliance with their specific requirements.
Read More : Cloud Market Share: A Look at the Cloud Ecosystem in 2023