Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information and virtual objects onto the real world. It is often used in mobile applications and wearable devices, and is designed to enhance the user’s perception of reality by adding computer-generated elements to their view of the physical world.
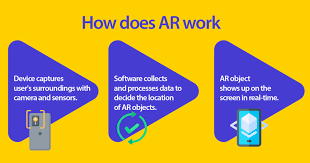
AR works by using a camera or other sensor to capture the user’s environment, and then processing this information to identify and track real-world objects. The system then overlays digital content onto these objects, creating the illusion that the virtual elements are part of the real world.
AR has a wide range of potential applications, from gaming and entertainment to education, marketing, and training. For example, AR can be used to create interactive educational experiences that allow users to explore and learn about real-world objects and environments in a more engaging and immersive way. In marketing, AR can be used to create virtual product demonstrations, allowing users to visualize products in their own environment before making a purchase. In the future, it is likely that AR technology will continue to evolve and become even more integrated into our daily lives.

How augmented reality works
Augmented reality (AR) works by overlaying digital information and virtual objects onto the real world. The process involves several steps, including:
- Sensing and tracking: The first step in AR is to sense and track the real world. This is typically done using a camera or other sensor that captures the user’s environment.
- Mapping and recognition: The next step is to map and recognize real-world objects. This involves identifying the location, orientation, and size of objects in the user’s environment.
- Rendering: Once the real-world environment has been sensed and mapped, the AR system can begin rendering digital content and virtual objects. This content is overlaid onto the user’s view of the real world, creating the illusion that the virtual elements are part of the real world.
- Display: The final step is to display the AR content to the user. This can be done using a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and head-mounted displays.
Overall, AR technology relies on a combination of sensors, tracking algorithms, and display technologies to create a seamless blend of the real and virtual worlds. The result is an immersive and interactive experience that can be used in a wide range of applications, from gaming and entertainment to education, training, and marketing.
The augmented reality platform that generates business and commercial benefits
There are several augmented reality platforms that can generate business and commercial benefits. Here are a few examples:
- ARKit and ARCore: These are the AR platforms developed by Apple and Google, respectively. They are designed to help developers create AR experiences for iOS and Android devices. These platforms can be used to create a wide range of AR applications, from gaming and entertainment to retail and marketing.
- Vuforia: This is an AR platform developed by PTC, which is designed for industrial and enterprise applications. Vuforia can be used to create AR experiences that enhance manufacturing, maintenance, and service operations.
- Wikitude: This is an AR platform that can be used to create location-based AR experiences. It allows developers to overlay digital content onto real-world locations, creating immersive and interactive experiences for users.
- Unity: This is a popular game development platform that can also be used to create AR experiences. Unity offers a wide range of tools and resources for developers, making it a popular choice for creating AR games and entertainment applications.
The choice of AR platform will depend on the specific needs of the business and the target audience for the AR application. It is important to consider factors such as ease of use, compatibility with different devices, and the availability of resources and support when selecting an AR platform for commercial use.
Read More : Top 7 Best Web Development Technologies to use in 2023 & Beyond
Augmented reality FAQ(s)
Q: What are some practical applications of augmented reality? A: Augmented reality has various practical applications across different industries. Some common applications include:
- Gaming and Entertainment: AR games like Pokémon Go have gained popularity, where virtual elements are superimposed on the real world for an interactive gaming experience. AR is also used in interactive storytelling, virtual tours, and immersive experiences in entertainment.
- Retail and E-commerce: AR allows customers to visualize products in their real environment before making a purchase. Virtual try-on for clothing and accessories, furniture placement, and product visualization are examples of AR in retail and e-commerce.
- Education and Training: AR enhances learning experiences by providing interactive and immersive content. It can be used for virtual experiments, anatomy visualization, historical reconstructions, and skills training in various fields.
- Manufacturing and Maintenance: AR can assist technicians and engineers by providing real-time guidance, overlaying instructions or data onto machinery or equipment. It can help streamline assembly processes, maintenance tasks, and remote assistance.
- Healthcare: AR has applications in medical training, surgery planning, and patient education. It can provide surgeons with real-time guidance during procedures, display patient data, or simulate medical scenarios.
- Architecture and Design: AR allows architects and designers to visualize and present 3D models of buildings or interior designs in the real environment. Clients can experience virtual walkthroughs, explore different design options, and assess spatial layouts.
Q: What devices are used for experiencing augmented reality? A: Augmented reality can be experienced through various devices, including:
- Smartphones and Tablets: Most smartphones and tablets have built-in cameras, sensors, and processing power required for AR applications. They are widely accessible and commonly used for AR experiences.
- Smart Glasses and Headsets: Dedicated AR devices like smart glasses and headsets provide a more immersive AR experience. Examples include Microsoft HoloLens, Google Glass, and various VR/AR headsets.
- Wearables: AR can also be integrated into wearables like smartwatches or fitness trackers, enabling users to receive contextual information on their wrist.
Q: What are markers or triggers in augmented reality? A: Markers or triggers in augmented reality are visual or physical elements that act as reference points for AR applications. These markers can be images, QR codes, symbols, or objects with distinct patterns. When detected by the AR system, they trigger the overlay of virtual content associated with the marker.
Q: Are there any safety considerations for augmented reality? A: Yes, there are safety considerations for augmented reality, such as:
- Physical Environment: Users should be aware of their surroundings to avoid accidents or collisions while engaged in AR experiences.
- Distraction: AR experiences can be immersive and may distract users from their immediate environment. It’s important to use AR responsibly, especially in situations requiring full attention, such as driving or operating machinery.
- Cybersecurity: AR apps may require access to personal data or have online connectivity. Users should exercise caution and be mindful of privacy and security settings.
- Motion Sickness: Some users may experience motion sickness or discomfort when using AR applications, particularly if the virtual content is not properly aligned with the real world.
Q: How can I develop augmented reality applications? A: Developing augmented reality applications typically involves a combination of programming languages, software development kits (SDKs), and tools specific to the platform or device. Some popular AR development frameworks include ARKit (iOS), ARCore (Android), Unity3D, Vuforia, and OpenCV. These frameworks provide libraries and APIs to build AR experiences. Learning programming languages like C#, Java, or Swift can also be helpful for AR development. Additionally, online tutorials, documentation, and communities dedicated to AR development can provide guidance and support
Read More : Will startups have a shot in the enterprise AI race?
Augmented reality impact on business
Augmented reality (AR) has a significant impact on businesses across various industries. Here are some ways AR is transforming business operations and creating value:
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: AR enables businesses to provide interactive and engaging experiences to customers. Retailers can use AR to allow customers to virtually try on products, visualize how furniture or decor items would look in their homes, or provide immersive product demonstrations. This enhances the shopping experience, increases customer engagement, and drives sales.
- Improved Training and Education: AR is being used in training programs to simulate real-life scenarios and provide hands-on experience. In industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and aviation, employees can learn complex tasks in a safe virtual environment. AR overlays instructional information, guidance, and feedback, improving training effectiveness and reducing errors.
- Streamlined Design and Prototyping: AR facilitates the design and prototyping processes by allowing designers and engineers to visualize 3D models in real-world contexts. Architects can overlay virtual building designs onto physical locations, enabling better visualization and assessment of structures. This leads to more accurate designs, efficient collaboration, and cost savings.
- Efficient Maintenance and Repair: AR aids technicians and field workers by providing real-time access to information and instructions during maintenance or repair tasks. By overlaying step-by-step guides or visual cues onto equipment or machinery, AR simplifies complex processes, reduces downtime, and improves productivity.
- Remote Collaboration and Support: AR enables remote collaboration by overlaying virtual elements onto a live video feed. Experts can provide remote assistance and guidance to field technicians or customers, reducing the need for physical presence and travel. This improves efficiency, accelerates problem-solving, and reduces costs.
- Data Visualization and Analytics: AR can present real-time data and analytics in a visual and intuitive manner. Business professionals can access and analyze complex data sets through AR dashboards, graphs, or interactive charts. This enhances decision-making processes and enables data-driven insights.
- Marketing and Branding: AR offers unique marketing opportunities by creating interactive and immersive brand experiences. Businesses can leverage AR for engaging advertising campaigns, interactive product launches, or location-based promotions. AR-powered games and experiences can drive customer engagement and brand loyalty.
- Remote Training and Meetings: AR facilitates remote training and virtual meetings by enabling participants to collaborate and interact in a shared virtual space. This is particularly valuable for distributed teams, enabling effective communication, knowledge sharing, and collaboration regardless of geographical locations.
Overall, augmented reality has the potential to transform business operations, improve customer engagement, optimize processes, and unlock new opportunities across industries. Its ability to blend the physical and virtual worlds creates innovative and impactful experiences that drive business growth and efficiency.